
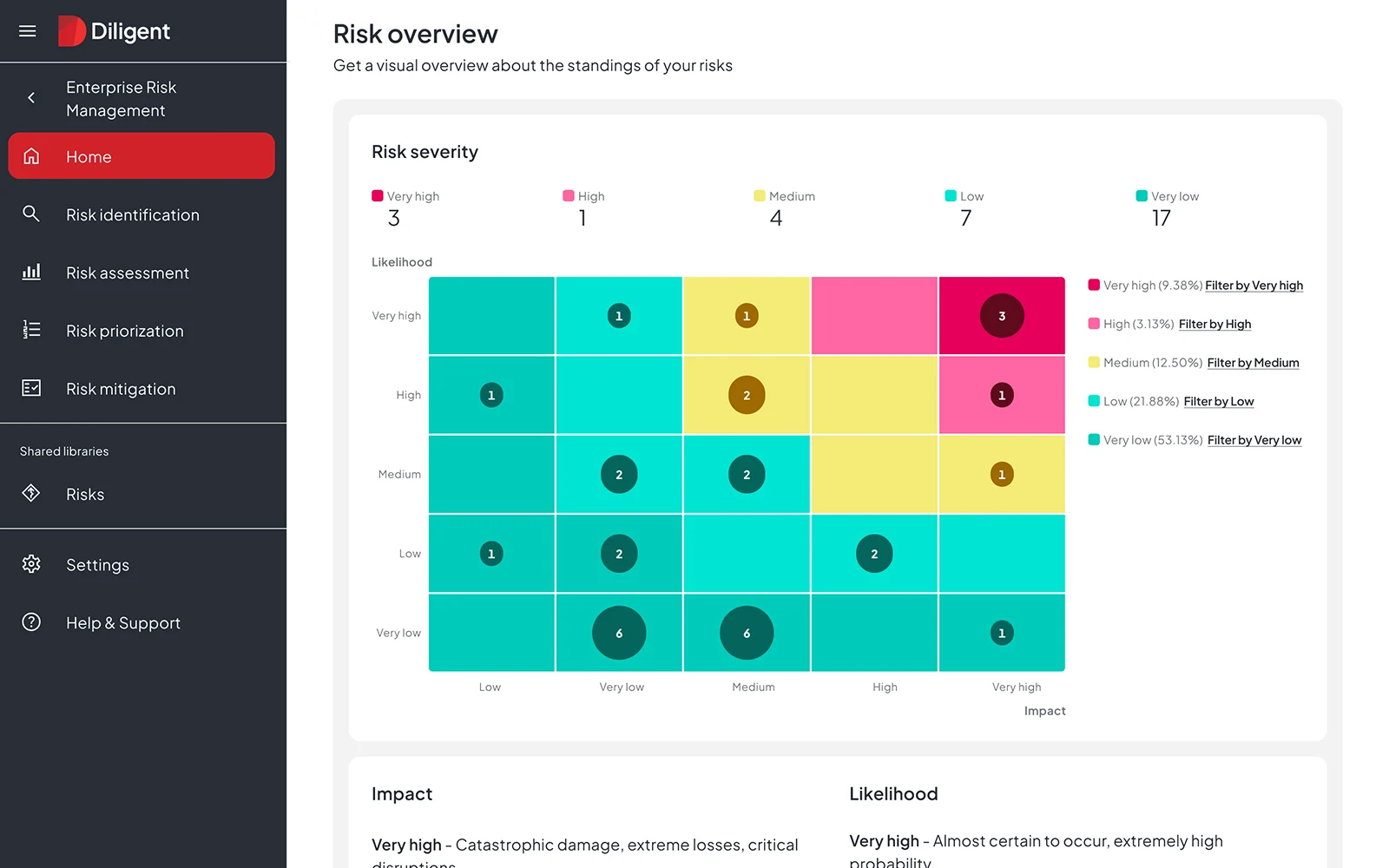
AI governance is emerging as one of the most pressing strategic challenges facing boards today. According to the Q4 2025 Business Risk Index conducted by Diligent Institute and Corporate Board Member, 60% of legal, compliance and audit leaders now cite technology as their top risk concern — well ahead of economic factors (33%) and tariffs (23%). Yet despite this urgency, only 29% of organizations have comprehensive AI governance plans in place.
"Boards are racing to harness AI's potential, but they must also uphold company values and safeguard the hard-earned trust of their customers, partners and employees," says Dale Waterman, Principal Solution Designer at Diligent.
The challenge is clear: How do organizations accelerate AI adoption to support transformational objectives while managing the risks and opportunities it creates? The answer lies in effective AI governance.
Here, we’ll explain how to develop an AI governance approach that helps you harness innovation without exposing your organization to undue risk, including:

AI governance encompasses the frameworks, policies and practices that promote the responsible, ethical and safe development and use of AI systems. It establishes the guardrails that enable innovation while protecting stakeholders from potential harm.
Boards will collaborate with key technology and risk stakeholders to set guidelines for transparency, accountability and fairness in AI technologies to prevent harm and bias while maximizing their benefits operationally and strategically. Responsible AI governance considers:
Corporate governance more broadly arose to balance the interests of all key stakeholders — leadership, employees, customers, investors and more — fairly, transparently and for the company's good. AI governance is similarly important because it prioritizes ethics and safety in developing and deploying AI.
“The corporate governance implications of AI are becoming increasingly understood by boards, but there is still room for improvement,” says Jo McMaster, Regional Vice President of Sales at Diligent.
Without good governance, AI systems could lead to unintended consequences, from discrimination and misinformation to economic and social disruptions. Having a strong AI governance approach:
Boards must balance competing priorities when overseeing AI: enabling innovation that drives competitive advantage while managing risks to data privacy, security and stakeholder trust.
"Have a candid assessment of what your board's capabilities are, what your C-suite's capabilities are. The board needs to apply an appropriate level of governance pressure to someone who's going to oversee the AI landscape, the risk exposure, the disruption and the opportunity," says Keith Enright, VP and Chief Privacy Officer at Google and Board Director at ZoomInfo.
Responsible AI governance requires boards to address five key areas:
Global AI regulations currently lack harmonization, creating complexity for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions. Some countries emphasize innovation and industry self-regulation, while others implement comprehensive legal frameworks with strict compliance requirements.
"During a time of regulatory uncertainty and ambiguity, where laws will lag behind technology, we need to find a balance between good governance and innovation to anchor our decision-making in ethical principles that will stand the test of time when we look back in the mirror in the years ahead," says Waterman.
Some significant frameworks around the world include:
The EU AI Act, which entered into force in 2024, represents the world's most comprehensive AI regulation. The law classifies AI systems into four risk categories:
The UK published an AI regulation white paper in 2023, emphasizing a pro-innovation, sector-based approach. Rather than instituting a single comprehensive law, the UK encourages industry self-regulation of ethical AI practices while focusing on safety, transparency and accountability. Sector-specific regulators provide guidance appropriate to their industries.
Since 2024, the government’s formal response and roadmap have strengthened this model by creating a central AI regulation “function” in government, tasking key regulators to publish AI strategies, and signalling future targeted, binding requirements for highly capable AI systems rather than an EU‑style horizontal AI Act.
The U.S. approach combines federal executive actions with state-level legislation. The Biden administration's 2023 Executive Order on AI reinforced safety concerns and established NIST's role in AI risk management.
However, federal AI legislation remains limited, leaving states to fill regulatory gaps. States including California, Colorado, Illinois and Utah have since adopted notable AI or automated‑decision laws, with Colorado’s 2024 comprehensive AI Act now delayed to June 2026 for implementation and California advancing detailed anti‑discrimination and employment‑AI rules.
China's New Generation Artificial Intelligence Plan represents one of the most detailed AI regulatory systems globally. It includes strict AI controls, safety standards and facial recognition regulations. The 2023 Interim Measures for AI Services require AI-generated content to align with Chinese social values and establish provider obligations for safety assessments and user protections.
Subsequent guidance and enforcement practice in 2024–2025 have focused on clarifying providers’ security‑assessment duties, content‑management responsibilities and the extraterritorial reach of the generative‑AI rules for services accessible in China, but the Interim Measures remain the core national framework.
Beyond regulations, industry bodies and standards organizations have developed technical AI governance guidelines. While voluntary, complying with relevant technical standards can help your organization foster quality, safe and efficient AI-powered products, services and innovation.

Most guidelines attempt to strike a balance between these easily conflicting interests. These include:
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework offers a flexible, voluntary approach to AI risk management. It addresses key governance concerns, including bias, explainability and security, through four core functions:
The International Organization for Standardization has released comprehensive AI standards addressing data management, algorithmic transparency and security:
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers established an AI committee in 2021, developing technical standards for AI governance within specific sectors. These industry-led standards focus on interoperability, safety testing and ethical AI development practices.
The ITU conducts focus groups assessing AI standards requirements for specific applications, including digital agriculture, natural disaster management, healthcare, environmental efficiency and autonomous driving.
Despite the value of AI governance, getting it right can be difficult. Standards must evolve as rapidly as technology does and consider the distinct regulatory approaches across jurisdictions — not to mention ethical concerns.
Boards working to govern AI may also need to confront:
AI governance should encompass more than specific processes for developing and using AI. Frameworks today should also consider five ethical principles to ensure AI is developed and deployed in a way that benefits society while minimizing harm. The principles below are also the foundation for emerging AI ethical guidelines.
An AI governance policy clearly outlines what an organization considers the acceptable development and use of AI systems. These guidelines should be clear, easy for employees to follow and align with compliance and risk management measures.
What these policies mandate can vary by organization. Some may prohibit entering proprietary information into AI systems; others may specify which tasks AI can support and which it can’t. Whatever the requirement, though, AI governance policies are important because they:
Given the quick pace of AI evolution, writing a governance policy can feel daunting. What does it look like to manage AI proactively and ethically? Here’s a template to get you started:
Effective Date: [MM/DD/YYYY]
Last Updated: [MM/DD/YYYY]
Owner: [AI ethics and compliance team]
1. Purpose
This AI Governance Policy outlines the principles, guidelines and responsibilities for the ethical development, deployment and management of AI within [Organization Name]. We aim to promote the responsible, fair and transparent use of AI while aligning with legal and ethical standards.
2. Scope
This policy applies to all AI systems [Organization Name] develops, procures or deploys, including machine learning models, automated decision-making tools and AI-driven analytics in business operations.
3. Governance principles
[Organization Name] commits to the following:
3.1 Fairness and bias mitigation
3.2 Transparency and explainability
3.3 Accountability and oversight
3.4 Privacy and data protection
3.5 Security and risk management
4. Compliance and legal standards
This policy aligns with the following regulatory frameworks:
5. Roles and responsibilities
6. AI risk assessments and audits
7. Continuous monitoring and policy updates
8. Reporting and incident response
9. Enforcement and consequences
10. Contact information
Effective AI governance starts with an implementation strategy that unites stakeholders across the board, the executive team and operational functions. Organizations can follow these steps to embed AI governance into their operations:
Define specific governing principles for AI aligned with your organization's values and risk tolerance. Consider how these principles connect AI governance with other essential functions like IT, legal and risk management. Determine how AI oversight fits into your overall governance structures at the board level.
Organizations increasingly begin by creating a comprehensive AI inventory that identifies all internal and third-party AI systems, including shadow AI that employees may be using without formal approval. Classify systems by risk level, use case and jurisdictional requirements using frameworks like the EU AI Act's risk categories or internal risk ratings.
Assign specific roles and responsibilities to avoid duplication and ensure comprehensive coverage:
"Put AI in your risk register. No one's going to argue with that. Get an AI policy. Board should be asking management for a policy," says Richard Barber, CEO of MindTech Group.
Roll out the pillars of your AI governance approach, including regular bias and fairness audits, reporting mechanisms for AI decisions, human oversight requirements for high-risk systems and data protection compliance measures.
Though the board maintains ultimate AI governance oversight, creating a dedicated committee with representatives from technology, legal, risk management and leadership makes policies more rigorous. The committee can define review processes for new AI developments and create training programs for employees and stakeholders.
Move beyond policy documents to platforms that execute AI governance in day-to-day operations. This includes dashboards for monitoring AI system performance, workflows for approval and risk assessment, control libraries aligned with regulatory frameworks and risk heatmaps that surface emerging concerns.
Lead regular risk assessments using frameworks like NIST AI RMF to identify emerging threats. Establish centralized dashboards for real-time AI monitoring. Review AI ethics and compliance updates quarterly to adapt governance policies as technology and regulations evolve.
Train employees on AI ethics and responsible usage, engaging them in protecting the organization. Establish clear mechanisms for reporting AI concerns, and consider AI ethics advisory boards to provide independent guidance. The most successful AI governance programs make responsible AI everyone's responsibility, not just a compliance function.
Effective AI governance goes beyond ethical principles to require structured policies, operational controls and continuous monitoring. Organizations working toward best-in-class AI governance should consider the following practices:
Paint a clear picture among the board and executives about what successful AI governance looks like. Then establish metrics to evaluate your program quantitatively and qualitatively. This could include fairness and bias metrics, scoring for AI output explainability, regulatory compliance rates and incident response effectiveness.
AI may need different governance at different stages. Consider how your governance framework specifically addresses risks and opportunities during development, testing and validation, deployment, ongoing monitoring and system retirement.
AI development, deployment and usage won't always go according to plan. Build fast-acting responses to model failures, security breaches, ethical concerns and other high-risk scenarios. User feedback loops help identify harms proactively before they escalate.
Diverse perspectives strengthen AI governance. Engage regulators, industry experts and internal stakeholders across functions. The chief risk officer may identify considerations the chief technology officer hadn't recognized; this cross-functional dialogue ultimately strengthens governance outcomes.
Integrate AI governance metrics into board reporting, including the number of high-risk AI systems without owners, time to remediate AI incidents and percentage of systems with documented risk classifications. This visibility keeps governance accountable at the highest levels.
The most comprehensive AI governance policy fails if employees aren't prepared to uphold it. Conduct AI ethics and governance training for developers, end users and leadership. Create transparency reports communicating the impact of governance efforts. The more you engage employees in responsible AI use, the stronger your governance posture becomes.
Manual governance processes struggle to keep pace with AI adoption's velocity and complexity. Spreadsheet-based policy tracking, email-driven risk assessments and document-based compliance reporting leave gaps that compromise oversight — often discovered only during audits or regulatory examinations.
"Technology risk is now the connective tissue across the entire risk register. We know that boards too are experimenting with new tech like AI tools to enhance oversight, yet relatively few organizations are leveraging AI-powered dashboards for risk monitoring. Closing that execution gap will separate leaders from laggards," says Kira Ciccarelli, Senior Manager of Research at the Diligent Institute.
Purpose-built governance platforms like Diligent eliminate this fragmentation, transforming reactive AI compliance into proactive governance excellence.
The Diligent One Platform unifies governance, risk and compliance functions into a single connected infrastructure — reducing the silos that allow AI governance gaps to go undetected. Within the platform, multiple solutions directly address the challenges that undermine AI oversight quality:
Diligent Boards streamlines board governance workflows and ensures AI oversight receives the strategic attention it requires:
"The AI enhancements will take that further. It's more automation and more insights — what can be drawn out of the information instead of just managing it," notes one customer in Diligent's Sagic case study, describing how AI-powered governance tools transform board operations.
Diligent ERM provides comprehensive enterprise risk management that integrates AI governance into your broader risk framework:
For organizations building AI governance programs with resource constraints, AI Risk Essentials delivers AI-powered peer benchmarking and training tools that accelerate program maturity in as little as seven days. The solution provides a practical pathway to professional AI governance without hiring consultants or building frameworks from scratch.
Diligent IT Compliance accelerates the certifications and frameworks that underpin effective AI governance:
These integrated capabilities ensure that AI governance moves from policy documents to operational reality — providing the accountability, transparency and oversight that regulators and stakeholders increasingly demand.
Whether you're establishing your first AI governance framework, preparing for EU AI Act compliance or demonstrating AI oversight maturity to investors, integrated governance technology provides the accuracy and efficiency that manual processes cannot match.
Book a demo to see how Diligent helps organizations transform their AI governance processes.
AI governance is a shared responsibility across multiple functions. Typically, a chief compliance officer, general counsel or dedicated AI governance team provides oversight, while the board retains ultimate accountability.
Chief technology officers lead technical governance, chief risk officers conduct risk assessments and legal counsel ensures regulatory compliance. All employees share responsibility through training and policy adherence.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework provides voluntary guidance for AI risk management through four core functions: govern, map, measure and manage. ISO/IEC standards like ISO/IEC 42001 provide certifiable management system requirements that organizations can use to demonstrate governance maturity through third-party audits.
Many organizations layer both approaches — using NIST for risk management methodology and ISO for certification-ready governance structures.
The EU AI Act requires organizations to classify AI systems by risk level and implement governance requirements proportionate to that risk. High-risk systems require conformity assessments, technical documentation, human oversight and incident reporting.
Organizations operating in EU markets or serving EU customers must align their AI governance programs with these requirements by August 2026 or face significant penalties.
Boards should ask management about the organization's AI inventory, how AI systems are classified by risk level, what controls are in place for high-risk applications, how incidents are detected and reported, the compliance roadmap for applicable regulations and who holds accountability for AI governance outcomes. Regular AI governance updates should be a standing board agenda item.
Schedule a demo to see how Diligent's integrated platform transforms AI oversight and improves company-wide governance.